Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Tokunaga, Kohei*; Takahashi, Yoshio*
Environmental Science & Technology, 51(16), p.9194 - 9201, 2017/08
Times Cited Count:46 Percentile:83.05(Engineering, Environmental)In the present study, we explore a new application of barite (BaSO ) as a sequestering phase for selenite (Se(IV)) and selenate (Se(VI)) ions from aqueous solutions due to the low solubility and high stability of barite. The uptake of Se(IV) and Se(VI) during coprecipitation with barite was investigated through batch experiments to understand the factors controlling effective removal of Se(IV) and Se(VI) from polluted water to barite. The uptake of Se(IV) by barite is dependent on pH, coexistent calcium ion, and sulfate concentration in the initial solution, possibly due to their effects on the chemical affinity and structural similarity. On the other hand, the uptake of Se(VI) by barite was strongly dependent on sulfate concentration in the initial solution, which is only related to the structural similarity. This study provides a good estimate of its ability to effectively remove Se(IV) and Se(VI) from aqueous solutions (more than 80%) under optimized experimental parameters.
) as a sequestering phase for selenite (Se(IV)) and selenate (Se(VI)) ions from aqueous solutions due to the low solubility and high stability of barite. The uptake of Se(IV) and Se(VI) during coprecipitation with barite was investigated through batch experiments to understand the factors controlling effective removal of Se(IV) and Se(VI) from polluted water to barite. The uptake of Se(IV) by barite is dependent on pH, coexistent calcium ion, and sulfate concentration in the initial solution, possibly due to their effects on the chemical affinity and structural similarity. On the other hand, the uptake of Se(VI) by barite was strongly dependent on sulfate concentration in the initial solution, which is only related to the structural similarity. This study provides a good estimate of its ability to effectively remove Se(IV) and Se(VI) from aqueous solutions (more than 80%) under optimized experimental parameters.
Inui, Masanori*; Hong, X.*; Matsusaka, Tetsuya*; Ishikawa, Daisuke*; Kazi, M. H.*; Tamura, Kozaburo*; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Utsumi, Wataru
Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 312-314, p.274 - 278, 2002/10
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:30.84(Materials Science, Ceramics)no abstracts in English
Kato, Hiroshige*; Mine, Tatsuya*; Mihara, Morihiro; Oi, Takao; Honda, Akira
JNC TN8400 2001-029, 63 Pages, 2002/01
Cementitious materials will be used for the TRU waste repository as a component of engineered barrier system. The distribution coefficients which represent the retardation of radionuclides migration for the cementitious materials would be one of the important parameter for the safety assessment. The much information of radionuclide sorption onto the cementitious materials has been accumulated through the study in the world. Therefore it is necessary to compile the information and Kd of the radionuclides reported in previous studies. In this report, the Kd of the important radionuclides, such as C, Ni, Se, Sr, Zr, Nb, Mo, Tc, Sn, I, Cs, Sm, Pb, Ra, Ac, Th, Pa, U, Np, Pu, Am, Cm, for the cementitious materials were compiled as the Sorption Database (SDB). For radionuclides to be sensitive to the redox potential, e.g. Se, Tc, Pa, U, Pu and Np, some Kds measured under the controlled atmosphere had been reported, and few Kds measured under the controlled redox potential had been reported. For Se, Mo, Sm, Cm and Ac, the distribution coefficients had not been reported, therefore distribution coefficients of Se and Mo for OPC (Ordinary Portland Cement) pastes were measured by batch sorption experiments and these data were added into the SDB.
Katayama, Yoshinori
Journal of Synchrotron Radiation, 8(Part2), p.182 - 185, 2001/03
no abstracts in English
Katayama, Yoshinori; Mizutani, Takeshi; Utsumi, Wataru; Shimomura, Osamu; Tsuji, Kazuhiko*
Physica Status Solidi (B), 223(2), p.401 - 404, 2001/01
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:66.81(Physics, Condensed Matter)no abstracts in English
Iida, Yoshihisa; Yamaguchi, Tetsuji; Nakayama, Shinichi; *; Sakamoto, Yoshiaki
Materials Research Society Symposium Proceedings, Vol.663, p.1143 - 1149, 2001/00
no abstracts in English
Mizutani, Akihiko; ;
JNC TN9400 2000-013, 66 Pages, 2000/02
Feasibility study on a self-consistent fuel cycle system has been performed in the nuclear fuel recycle system with fast reactors. ln this system, the self-generated MAs (Minor Actinides) and LLFPs (Long-Lived Fission Products) are confined and incinerated in the fast reactor, which is called the "Equilibrium Core" concept. However, as the isotope separations for selected LLFPs have been assumed in this cycle system, it seems that this assumption is far from realistic one from the viewpoint of economy with respect to the fuel cycle system. ln this study, the possibility for realization of the "Equilibrium Core" concept is evaluated for three fuel types such as oxide, nitride and metallic fuels, provided that the isotopic separation of LLFPs is changed to the element one. This study provides, that is to say, how many LLFP elements can be confined in the "Equilibrium Core" with element separation. This report examines the nuclear properties of the "Equilibrium Core" for various combinations of LLFP incineration schemes from the viewpoints of the risk of geological disposal and the limit in confinable quantity of LLFPs. From the viewpoint of the risk of geological disposal estimated by the retardation factor, it is possible to confine with element separation for T , I and Se even in the oxide fueled core. From the standpoint of the limit of confinable amounts of LLFPs, on the other hand, T
, I and Se even in the oxide fueled core. From the standpoint of the limit of confinable amounts of LLFPs, on the other hand, T , I, S
, I, S , S
, S and Cs can be confined with element separation in case that the nitride fuel is chosen.
and Cs can be confined with element separation in case that the nitride fuel is chosen.
Ijiri, Yuji; ; *; Watari, Shingo; K.E.Web*; *; *
JNC TN8400 99-092, 91 Pages, 1999/11
JNC has been developed the performance assessment approaches for both fractured rock and porous rock. An equivalent continuum model is incorporated for solving the radionuclide migration in porous rock, while a discrete fracture network model is incorporated for solving the radionuclide migration in fractured rock (see more detail in Sawada et al. [1999]). This report describes the methodology, the data and the results of the performance assessment of porous rock. From the results of radionuclide migration analyses that were based on the hydrogeological properties obtained from the Neogene sedimentaly rock at the Tono mine, it was found that the release rate of selenium-79 and cesium-135 are dominant in porous rock. The sensitivity analyses using one-dimensional porous model revealed that hydraulic conductivity has more influences on the results than porosity does. In addition, it was found that smaller distribution coefficients of sandstone yield higher release rate than mudstone and tuff, and smaller distribution coefficients of saline water conditions yield higher release rate than fresh water conditions. The radionuclide migration in Neogene sedimentaly rock, where flow in rock matrix as well as in fractures are significant, was evaluated by superposing the results of porous model and fracture model. Since fracture model tends to yield more conservative results than porous model, it is obvious that the performance of Neogene sedimentary rock can be conservatively assessed by fracture model alone. The nuclide migration analyses performed in this report were based on the hydrogeological properties obtained at the depth between 20 meters and 200 meters frrom the ground surface. Therefore, it should be noted that the release rate at the depth of a future repository in Neogene sedimentary rock, 500 m, will be smaller than that shown in this report due to peemeability decrease from 200 m to 500 m.
Katayama, Yoshinori
Hoshako, 12(5), p.375 - 383, 1999/11
By combining large volume presses and synchrotron radiation, it is now possible to study structure of liquids under high-pressure and high-temperature. In addition to the X-ray diffraction method, EXAFS is also now applicable to samples under high-pressure. We have also developed a new method for density measurements under high-pressure. These methods are used to study structural change in liquid selenium that is associated with a semiconductor-to-metal transition. X-ray diffraction study on liquid phosphorus reveals that there are two distinct liquid forms in phosphorus.
Sato, Haruo
JNC TN8400 99-062, 16 Pages, 1999/10
Effective diffusion coefficients (De) for Ni , Sm
, Sm , Am
, Am and SeO
and SeO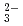 were measured as a function of the ionic charge of diffusion species to quantitatively evaluate the effect of ionic charge in compacted bentonite. The De measurements for Ni
were measured as a function of the ionic charge of diffusion species to quantitatively evaluate the effect of ionic charge in compacted bentonite. The De measurements for Ni and Sm
and Sm were carried out for a bentonite dry density of 1.8 Mg
were carried out for a bentonite dry density of 1.8 Mg m
m with a simulated porewater condition of pH5
with a simulated porewater condition of pH5 6 by through-diffusion method. The De values for SeO
6 by through-diffusion method. The De values for SeO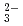 were measured for a bentonite dry density of 1.8 Mg
were measured for a bentonite dry density of 1.8 Mg m
m with a simulated porewater condition of pH11. The De measurements for Am
with a simulated porewater condition of pH11. The De measurements for Am were carried out for the dry densities of 0.8, 1.4 and l.8 Mg
were carried out for the dry densities of 0.8, 1.4 and l.8 Mg m
m with a porewater condition of pH2 in order to check cation exclusion. Sodium bentonite, Kunigel-V1 was used for those measurements. For the measurements of Am, H-typed Kunigel-V1 which interlayer ion (Na
with a porewater condition of pH2 in order to check cation exclusion. Sodium bentonite, Kunigel-V1 was used for those measurements. For the measurements of Am, H-typed Kunigel-V1 which interlayer ion (Na ) was exchanged with H
) was exchanged with H was used, because the experiments are carried out for a low pH range. The order of obtained De values was Sm
was used, because the experiments are carried out for a low pH range. The order of obtained De values was Sm
 Ni
Ni
 Am
Am
 SeO
SeO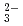 . These De values were compared to those reported to date. Consequently, the order of De values was Cs
. These De values were compared to those reported to date. Consequently, the order of De values was Cs
 Sm
Sm
 HTO
HTO  Ni
Ni
 anions (I
anions (I , Cl
, Cl , CO
, CO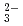 , SeO
, SeO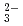 TcO
TcO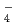 , NpO
, NpO CO
CO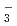 , UO
, UO (CO
(CO )
)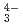 ), showing a tendency of cations
), showing a tendency of cations  HTO
HTO  anions. Only the De values of Am
anions. Only the De values of Am were approximately the same degree as those of anions. The reason that the De of Ni
were approximately the same degree as those of anions. The reason that the De of Ni was lower than that of HTO may be because the free water diffusion coefficient (Do) of Ni
was lower than that of HTO may be because the free water diffusion coefficient (Do) of Ni is about 1/3 of that of HTO. The cause that the De of Am
is about 1/3 of that of HTO. The cause that the De of Am was approximately the same degee as those of anions may be because the Do of Am
was approximately the same degee as those of anions may be because the Do of Am is about 1/3 of that of HTO and that Am
is about 1/3 of that of HTO and that Am was electrostatically repulsed from the surface of bentonite by cation exclusion. The formation factors (FF), calculated normalizing Do, were in the ...
was electrostatically repulsed from the surface of bentonite by cation exclusion. The formation factors (FF), calculated normalizing Do, were in the ...
Sato, Haruo
JNC TN8400 99-060, 12 Pages, 1999/10
Apparent diffusion coefficients(Da) of Cs(Cs ), Ni(Ni
), Ni(Ni ) and Se(SeO
) and Se(SeO
 ) in a Na-bentonite (Kunigel-V1) were measured for a dry density of 1.8 Mg
) in a Na-bentonite (Kunigel-V1) were measured for a dry density of 1.8 Mg m
m with silica sand of 30 wt% at room temperature by in-diffusion method to evaluate the effect of the mixture of silica sand on Da in bentonite. The experiments for Cs and Ni were carried out under aerobic condition, but those for Se which is redox sensitive were carried out in an Ar glove-box (O
with silica sand of 30 wt% at room temperature by in-diffusion method to evaluate the effect of the mixture of silica sand on Da in bentonite. The experiments for Cs and Ni were carried out under aerobic condition, but those for Se which is redox sensitive were carried out in an Ar glove-box (O concentration
concentration  0.1 ppm). Consequently, no significant effect of silica sand mixture to the bentonite on Da values of Cs and Se was found, and the obtained Da values were approximately the same as those in the system without silica sand reported so far. On the other hand, Da values of Ni in bentonite with silica sand were 2 orders of magnitude lower than those in bentonite without silica sand obtained to date. The Da values of Ni reported so far were obtained using stable isotopic tracer and a tracer solution with fairly high Ni concentration compared with concentration used in this study was introduced. Additionally, it is known that distribution coefficient (Kd) of Ni on Na-montmorillonite which is the major constituent clay mineral of Kunigel-V1 decreases with increasing Ni concentration. Based on this, the abrupt decrease in Da values of Ni for bentonite with silica sand is considered to be due to the difference of sorption caused by the difference of Ni concentration in the porewater of bentonite.
0.1 ppm). Consequently, no significant effect of silica sand mixture to the bentonite on Da values of Cs and Se was found, and the obtained Da values were approximately the same as those in the system without silica sand reported so far. On the other hand, Da values of Ni in bentonite with silica sand were 2 orders of magnitude lower than those in bentonite without silica sand obtained to date. The Da values of Ni reported so far were obtained using stable isotopic tracer and a tracer solution with fairly high Ni concentration compared with concentration used in this study was introduced. Additionally, it is known that distribution coefficient (Kd) of Ni on Na-montmorillonite which is the major constituent clay mineral of Kunigel-V1 decreases with increasing Ni concentration. Based on this, the abrupt decrease in Da values of Ni for bentonite with silica sand is considered to be due to the difference of sorption caused by the difference of Ni concentration in the porewater of bentonite.
Inui, Masanori*; Tamura, Kozaburo*; Oishi, Yasufumi*; Nakaso, Ichiro*; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Utsumi, Wataru
Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 250-252(Part2), p.519 - 524, 1999/08
no abstracts in English
Katayama, Yoshinori; Shimomura, Osamu; Tsuji, Kazuhiko*
Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 250-252(Part2), p.537 - 541, 1999/08
no abstracts in English
; Kaburaki, Hideo; *; *
Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 250-252(2), p.433 - 436, 1999/00
no abstracts in English
Ueta, Shinzo*
PNC TJ1211 98-002, 46 Pages, 1998/02
None
Ueta, Shinzo*
PNC TJ1211 98-001, 824 Pages, 1998/02
None
Katayama, Yoshinori*; Tsuji, Kazuhiko*; *; *
Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 232-234(Part2), p.93 - 98, 1998/00
no abstracts in English
Tsuji, Kazuhiko*; Katayama, Yoshinori
Physics of Complex Liquids, p.83 - 97, 1998/00
Structural changes with pressure for liquid Se and liquid Te have been studies. X-ray diffraction and extended x-ray absorption fine structure (EXAFS) have been measured at pressure up to 8 GPa by using a cubic-type multianvil apparatus and synchrotron radiation. With increasing pressure, the interchain atomic distance becomes short and approaches to the interchain atomic distance in liquid Se. In metallic liquid Se, two kinds of bonds coexist; shot bond and lond bond. The fraction of short bond decreases with increasing pressure, indicating weakening and breaking of covalent bonds. The structure of liquid Se under high pressure is similar to that of metallic liquid Te at atmospheric pressure. These results are discussed in connection with semiconductor-to-metal transitions in liquid Se, liquid Te and liquid Se Te
Te alloys with pressure, temperature and concentration.
alloys with pressure, temperature and concentration.